Reverse Osmosis (RO) is a technology used to remove a large majority of contaminants from water by pushing the water under pressure through a semi-permeable membrane(called reverse osmosis membrane).

Reverse osmosis removes contaminants from unfiltered water, or feed water, when pressure forces it through a semipermeable membrane. Water flows from the more concentrated side (more contaminants) of the RO membrane to the less concentrated side (fewer contaminants) to provide clean drinking water. The water produced is called filtered water. The concentrated water left over is called wastewater.

A semipermeable membrane has small pores that block contaminants but allow water molecules to flow through. In osmosis, water becomes more concentrated as it passes through the membrane to obtain equilibrium on both sides. Reverse osmosis, however, blocks contaminants from entering the less concentrated side of the membrane. For example, when pressure is applied to a volume of saltwater during reverse osmosis, the salt is left behind and only clean water flows through.
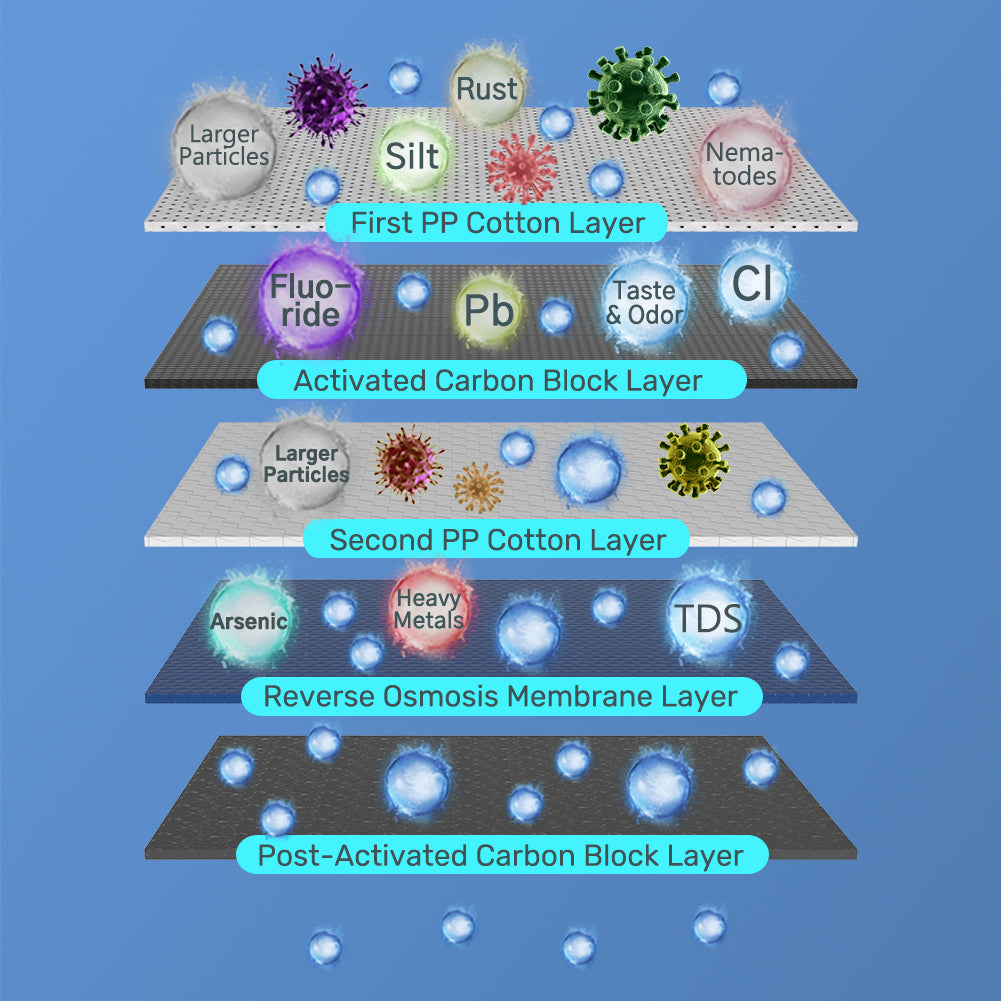
The precision of the reverse osmosis membrane is 0.0001 micron, so it can effectively remove dissolved salts, colloids, microorganisms, organic matter and so on, and is used in both industrial processes and the production of potable water.
Substances that reverse osmosis membranes can remove, including:
Lead
Arsenic
Copper
Nitrates and nitrites
Chromium (hexavalent & trivalent)
Selenium
Fluoride
Radium
Barium
Cadmium
Cyst (cryptosporidium)
Total dissolved solids (TDS)

The reverse osmosis system can remove unwanted sodium, other contaminants and dissolved solids, even some reverse osmosis system like Besdor AWater1 system, which adds minerals by post activated carbon to improve the taste. AWater1 reverse osmosis water filter system must be an ideal choice for most households.